Amino acids
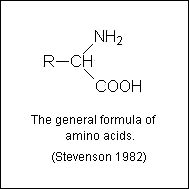
- As free amino acids
- in the soil solution
- in soil micropores
- As amino acids, peptides or proteins bound to clay minerals
- on external surfaces
- on internal surfaces
- As amino acids, peptides or proteins bound to humic colloids
- H-bonding and van der Waals' forces
- in covalent linkage as quinoid-amino acid complexes
- As mucoproteins
- As a muramic acid
Amino sugars
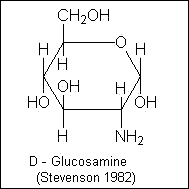
Nucleic Acids
Nitrogen transformation
Except under unusual circumstances, both mineralization and immobilizationalways function in soil, but in opposite direction.
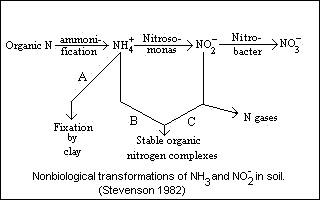
Chemical reaction of ammonia and nitrite with organic matter
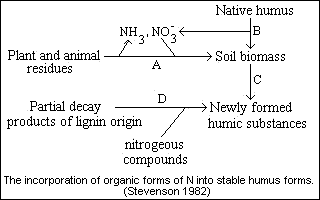
Stability of soil organic nitrogen
1. Proteinaceous constituents are stabilized through their reaction withother organic constituents, such as lignins, tanins, quinons.2. Biologically resistant complexes are formed in soil by chemical reactionsinvolving NH3+ or NO2- with lignins or humic substances.
3. Adsorption of organic N compounds by clay minerals (pariculary montmorillinitic types) protects the molecule from decomposition.
4. Complexes formed between organic N compounds and polyvalent cations, such as Fe, are biologically stable.
5. Some of the organic N occurs in small pores or voids and is physicallyinaccessible to microorganisms.